

Appointment Call
In case of any kind of emergency, which is related to asthma and allergy, you can call this number, the facility will be made available to you.
Advanced Allergy Testing Machines
Today Dr. Jafrey is one of the few selected doctors of India who are using advanced machines for 100% Best results of asthma and allergies.
For Immediate Assistance
Call Our Emergency Number
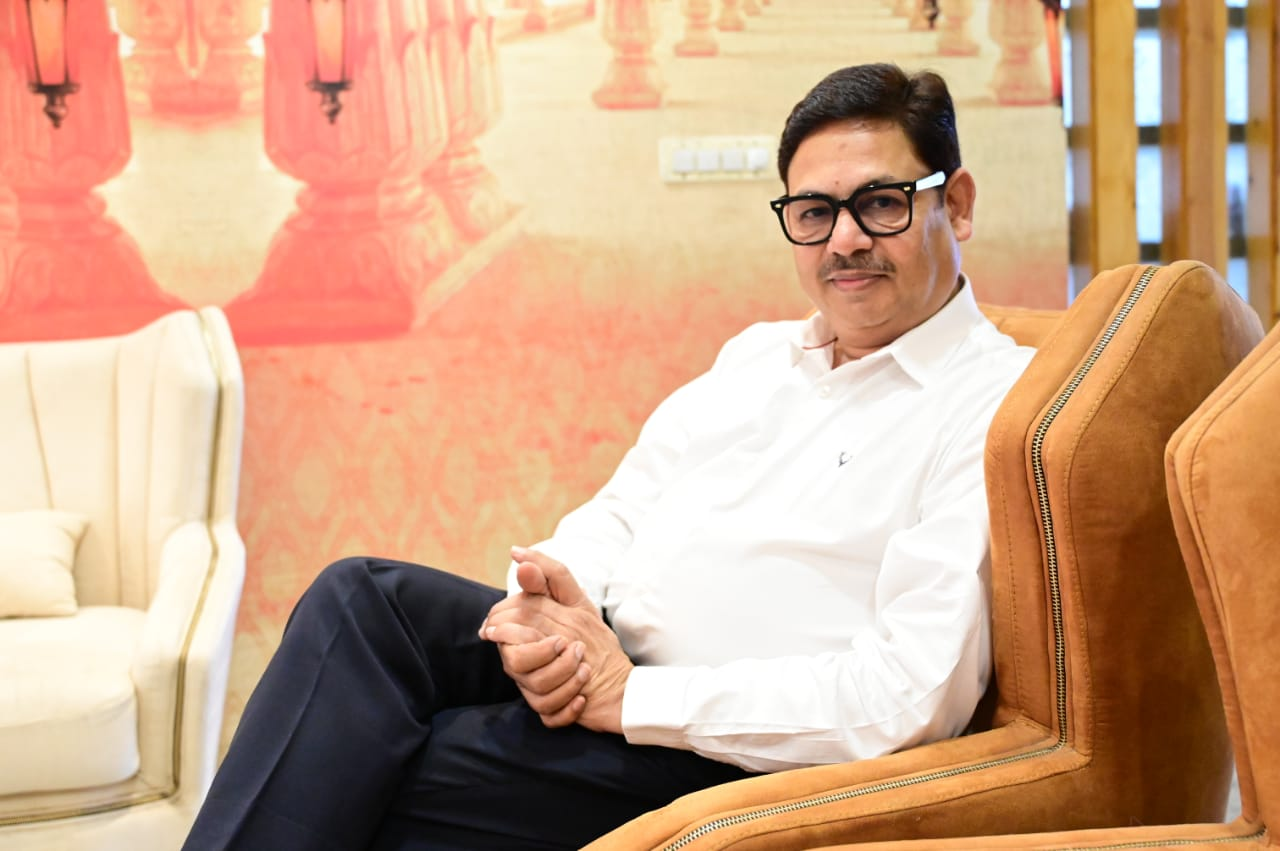
Dr S Z JAFREY has received acknowledgements as
“Most Inspiring Pulmonologist in India” by Economic Times at Delhi -2019
“Certificate of out standing work by Prajatantra First Print News Daily -2019 at Indore
“Certificate of Excellence” by Dainik Bhasker -2018 at Indore
“Excellence award in Allergy & Chest Diseases” by My FM – 2017 Radio at Indore “Inspiring Chest Specialist of India – 2024 at Times Now

Often referred as Bronchial Asthma, Shortness of breath, Breathlessness, Bronchitis, COPD etc. Asthma are mostly allergic in nature and affects fitness of patient.

Also called Sinus with history of Sneezing, Running nose, Itching in Nose, Stuffy nose & Often associated with headache, mental irritation and fatigue. Often misdiagnosed as Migraine, Anxiety.

Allergic Conjunctivitis is a allergic disease of eye where symptoms are redness of eyes, itchy eyes, watery eyes. This leads to irritating symptoms. Redness of eye is often annoying.

Eczema is often referred as Atopic dermatitis. Atopic means Allergic. Dermatitis means skin.This means an allergic skin disease.

Many persons have food allergy but are not aware. ‘gas’ ‘flatulency’ ‘acidity’ ‘post food distention of abdomen’, indigestion, constipation, frequently loose motions.

Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs.
But may spread to other organs. India has highest incidence in world.
Working Experience
Satisfied Patient
He was the first doctor to introduce many new techniques, machines in MP & CG. His vast knowledge has brought thing to this level. He has taught most of doctors about asthma, allergy in Indore and around. We have an edge over others. It’s a “TRUE CENTER of Asthma & Allergy” means all facilities related to diagnosis, treatment and teaching are available under one roof. WE are proud to claim that we are the pioneer since 2002 and only one till date to have 3 different world class allergy testing machines. These machine does blood allergy test.

Follow us on Instagram

Aware More About Allergy and Asthma Diseases on Our YouTube Channel

Happy Patients
Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Meri daughter ko bachpan se hi Sardi, khansi, chalne me sans fulti thi, naak behna, Sardi jyada hone se ankh me khujli hoti thi, cough bhi kafi jyada Ata tha, fan ki hawa bhi bilkul suit nhi hoti thi. Sans ki itni problem thi ki exam Tak bachhi ka chhodna pada tha. Fir sir relative se apka pta chala. Allergy test se pta chla gajar ghas dhul mitti ki allergy nikli. Vaccine lene ke 2 dose bad hi fayda mil gya. Bohot jagah ilaj karwane k bad fayda sirf apke treatment se hi Mila. Apki medicine or vaccine meri daughter ke liye kafi Aram dayak hai. Me allergy patients ko apka hi recommend krungi. Thankyou so much sir. Meri daughter ko thik krne ke liye.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. बहुत-बहुत शानदार क़ाबिल डाक्टर zafri जी ने मेरी बेटी का allergy का बेहतरीन इलाज किया और हम इनके इलाज से 100% संतुष्ट हैं. यहां मरीज की समस्या को बहुत शालीनता से सुनकर सभी टेस्ट, वैक्सीन , दवा का पूर्ण इंतजाम है.मेरे जैसे कई मरीज 700 - 800 km दूर से चलकर इलाज कराने यहां आते हैं thank you Dr. साहब..Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I had the pleasure of being treated by Dr. S.Z. Jafrey, a chest and allergy specialist, and I couldn't be more grateful for the care I received. In 2022, when my allergy symptoms were at their peak, I sought his help. The treatment he provided was not only effective medically but also came with an exceptional level of mental and emotional support. Dr. Jafrey treated me like his own daughter during one of the most challenging and depressing phases of my life. His compassionate and empathetic approach was truly a light of motivation for me. He went beyond the usual medical care to connect with me on an emotional level, which made a significant difference in my overall well-being. The facility where Dr. Jafrey practices is also excellent. It is clean, well-maintained, and the staff are friendly and professional, contributing to a positive overall experience. In my opinion, a good doctor is not just someone who treats the physical symptoms but also understands and supports the emotional and mental needs of their patients. Dr. Jafrey embodies this ideal perfectly. He provides the kind of holistic care that is much needed in today's world, where many people are suffering not just physically, but mentally as well. I highly recommend Dr. Jafrey to anyone in need of a chest and allergy specialist. His dedication to his patients' overall health and his ability to connect on a personal level make him an outstanding healthcare provider.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. 8- 10 sal se allergy se kafi pareshan tha, chhink khansi ana , ankho me khujli hoti thi bohot ansu ate the, sans chalti thi bohot jagah. Kai jagah treatment lia gwalior Ujjain kahi fayda nahi mila. Fir apke pas akr allergy test karwaya dust allergy smoke ki insect ki or khane ki allergy nikli. But apke vaccine kr 2 3 dose se hi bohot achha fayda mila. Medicine bhi lene ki jarurat nahi padti ab. Thankyou so much sir for this better treatment and better vaccinePosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Mere son ko last year garmi me urticaria ki problem start ho gai thi. Khujli chalna, bade bade laal chakte ho jate the baki Dr ko bataya to jb tk medicine chalti thi tab Tak hi relief tha, ayurvedic treatment bhi lia koi fayda nahi mila. Fir YouTube par apka video dekh kr apse treatment lene se. Food allergy batai apne. But I must say sir apke treatment se hi fayda mila h . Thankyou so much sir.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. 1 sal pehle sine me dard hota tha, balgam Banta tha, jakdan mehsoos hoti thi. Pehle problem kam thi bt 1 sal se bad gai thi. Thand k time jyada dikkat hoti thi. Fir July me apko dikhya. Apki vaccine se lene ke 1 month bad se hi me bilkul swasth mehsoos kar rha hoon. Thankyou so much sirPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Mera beta abhi 6 sal ka hai. 3 sal ki umra se isko sans lene me taklif, naak jam jati thi rat bhar nahi so pata tha. Allergy test krwane se pata chala dhul mitti ki allergy or jyadatar khane ki gar chij se allergy nikli. 6 7 month pehle hi apko dikhaya or ab Mera beta bilkul swasth h vaccine se bohot fayda Mila. Dawaiyo se bohot fayda Mila. Dhanyawad sir apki wajah se hi thik hi paya hai.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr Jaffrey is best allergy doctors in india
My Journey
















Our Direction
174 ED Eastern Ring Road (Between Robot and Khajrana Square) Indore
MP, India – 452016
Telephone:
0731-4064786 (10am-6pm IST)
Sunday and Major Holidays Closed
Pharmacy No: +91 8889777277
Appointment No: +91 8889777077
Emergency No: +91 9300001393

Chest & Allergy Centre - Best Pulmonologist | Chest Specialist | Lungs Doctor | Indore
+91 88897 77177